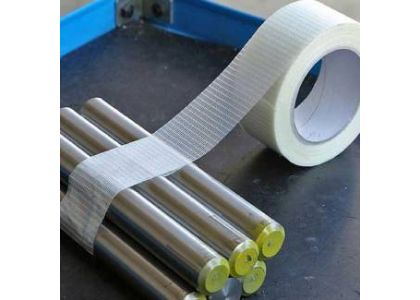
Filament reinforced strapping tape—also known as filament tape or strapping tape—combines continuous fiberglass filaments embedded in a pressure-sensitive adhesive coated onto a biaxially oriented film, delivering exceptional tensile strength and tear resistance in applications far beyond carton sealing. This guide explores its composite construction, key performance metrics, best practices for application, dispenser options, environmental and safety considerations, economic impact, real-world case studies, and an implementation framework. Packaging, construction, electronics, and logistics professionals will find actionable insights to leverage advanced filament tapes for stronger bonds, faster throughput, and measurable ROI.
Filament reinforced strapping tape consists of a polypropylene or PET backing stretched biaxially to align polymer chains and enhance dimensional stability. Continuous fiberglass filaments—5–10 µm in diameter and spaced 2–3 mm apart—are laid into a uniform adhesive layer, forming a microscopic grid that arrests tear propagation and distributes tensile loads evenly across the tape’s width. An optional clear polymer overcoat protects filaments from abrasion and moisture, extending service life in demanding environments. Specialized grades can withstand break loads up to 600 lbf/in (100 N/mm), outperforming standard carton tapes by over 300%.
In modern construction, reinforced filament packing tape is used to stabilize prefabricated panels and secure structural steel during hoisting.Bi-directional filament packing tape—with fibers oriented in both machine and cross directions—provides tear and cut resistance when binding pipes, formwork, and scaffolding components. Extra wide filament packing tape (up to 4 inches) spans large surface areas such as insulation boards or sheet goods, eliminating seams and weak points.Case studies show that replacing metal banding with reinforced filament tape reduced installation time by 20% and lowered material costs by 35%.
Filament reinforced packing tape secures printed circuit boards (PCBs) and delicate modules during high-speed assembly, minimizing misalignment and vibration damage. Its smooth backing prevents particulate contamination, while uniform fiberglass reinforcement maintains consistent pressure across the component surface. In large-module assembly—such as chassis or battery packs—extra wide filament packing tape ensures even load distribution, reducing rework by up to 15%.
Filament strapping packing tape is integral to securing heavy or irregular loads on pallets, crates, and in shipping containers. Its high tensile strength (200–300 N/cm in standard grades) allows carriers to cut wrap counts by 30%, saving both material and labor. Automated palletizing systems frequently deploy bi-directional fiber tapes for uniform tension control, enabling throughput over 100 pallets per hour with minimal manual intervention.
Key performance indicators include tensile strength, tear propagation resistance, adhesive peel, and shear retention.ASTM tests confirm break loads from 200 to 600 N/cm and tear-stop thresholds above 50 N, preventing small nicks from becoming full-roll failures.High-tack acrylic adhesives sustain bonds through UV exposure and temperature extremes, critical for outdoor and refrigerated storage. These attributes translate to up to 30% material savings and a 25–40% increase in packing line speed when paired with automated dispensers.
Surface Preparation: Wipe surfaces clean of dust, oil, and debris to maximize adhesive contact.
Filament Orientation: Align fibers with primary load directions for optimal pull-apart strength.
Tension Control: Apply 30–50 N draw force to seat filaments without overstretching the backing.
Overlap Strategy: Use 50% overlap on each pass to cover potential weak zones and distribute stress uniformly.
Edge Sealing: Firmly press tape edges to prevent lift and ingress of contaminants, preserving long-term seal integrity.
Handheld Tension-Adjustable Guns: Offer precise control for intermittent or mixed-size tasks.
· Bench-Mounted Dispensers: Accommodate tapes from 25 mm to 75 mm wide, suiting mid-volume packing areas.
Semi-Automatic Table-Top Machines: Motorized feed and cut deliver exact lengths and tensions, boosting throughput.
Fully Automated Inline Systems: Integrate with conveyors and robotics for rates above 100 cartons/min and programmed tension profiles.
Mixed polymer-glass tape constructions present recycling challenges, as adhesives hinder fiber recovery in standard streams. Partner with suppliers on take-back or mechanical separation programs to reclaim backing and fibers for reuse. High tensile characteristics also mean fewer wraps and less waste overall. Glass filaments can create sharp edges—require cut-resistant gloves and machine guards during handling.
Although carrying a 20–50% premium over standard carton tapes, filament reinforced tapes often yield payback in 2–4 months through reduced damage claims, labor savings, and lower disposal fees. Case data show up to a 30% drop in damage claims for national carriers and a 15% reduction in electronics assembly halts post-adoption.
A Midwest contractor replaced metal banding with filament tape, cutting labor by 20% and hardware costs by 35%.
An electronics OEM saw a 15% decrease in production stoppages after using fiber tape for PCB stabilization.
A national logistics hub reported a 30% reduction in load damage and a 40% throughput increase on automated pallet lines.
Pilot Program: Test on representative SKUs to benchmark metrics.
Data Tracking: Monitor seal failure rates, tape usage, waste volumes, and throughput.
SOP Development: Document prep, wrap patterns, dispenser settings, and safety protocols.
Supplier Partnerships: Secure service levels for quality, delivery, and sustainability initiatives.
Continuous Review: Conduct quarterly audits to refine application parameters or explore new variants.